Steam Hose Safety Facts
Handling steam is a very hazardous situation. Using care and some safety precautions can minimize or eliminate personal or property damage.
Selecting and Using Steam Hose

1. Make sure steam hose is identified as a steam hose. It should be branded as such, stating working pressure and temperature rating.
2. Make sure working pressure and temperature is not exceeded.
3. Do not allow hose to remain under pressure when not in use.
4. Avoid excess bending or flexing of hose near the coupling. Straight line operation is preferred. If bends are necessary as part of operation, spring guards may help.
5. Be sure to use recommended steam hose couplings and clamps on hose.
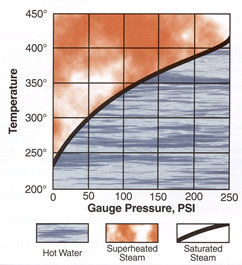
Steam Hose Chart
| Saturated Steam | |
| Gauge Pressure (psi) | Temperature of Saturated Steam (°F) |
| 10 | 239 |
| 25 | 267 |
| 50 | 298 |
| 75 | 320 |
| 100 | 338 |
| 125 | 353 |
| 150 | 366 |
| 175 | 377 |
| 200 | 388 |
| 225 | 397 |
| 250 | 406 |
Maintenance of Steam Hose
1. Periodic inspection of hose should include looking for cover blisters and lumps.
2. Check for kinked areas that could damage hose.
3. Drain hose after each use to avoid tube damage before hose is put back in operation, to avoid "pop corning" of the tube.
4. Check tightness of clamp bolts after each use.
5. Check to see if clamp halves are touching. If they are, recouple hose with smaller clamps to insure proper tightness or grip around hose.
6. Do not store hose over hooks.
7. Steam hose lying on metal racks or installed around steel piping will dry out the hose, causing tube and cover cracking.
8. For service in sub-zero applications, use only T331 Chlorobutyl hose.
Temperature of Saturated Steam
| Gauge Pressure | Temperature | Gauge Pressure | Temperature | ||||||||
| Ibl/ m2 | Kgf/ cm2 | Atm | Bar | °C | °F | Ibl/ m2 | Kgl/ cm2 | Atm | Bar | °C | °F |
| 25 | 1.76 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 130 | 267 | 120 | 8.44 | 8.16 | 8.28 | 177 | 350 |
| 30 | 2.11 | 2 | 2.1 | 134 | 274 | 140 | 9.84 | 9.52 | 9.66 | 182 | 361 |
| 35 | 2.46 | 2.4 | 2.4 | 138 | 281 | 160 | 11.25 | 10.9 | 11 | 188 | 371 |
| 40 | 2.81 | 2.7 | 2.8 | 141 | 287 | 180 | 12.65 | 12.2 | 12.4 | 193 | 379 |
| 45 | 3.16 | 3.1 | 3.1 | 144 | 292 | 200 | 14.06 | 13.6 | 13.8 | 198 | 388 |
| 50 | 3.52 | 3.4 | 3.5 | 148 | 298 | 225 | 15.82 | 15.3 | 15.5 | 203 | 397 |
| 60 | 4.22 | 4.1 | 4.1 | 153 | 307 | 250 | 17.58 | 17 | 17.3 | 208 | 406 |
| 70 | 4.92 | 4.8 | 4.8 | 158 | 316 | 275 | 19.33 | 18.7 | 19 | 212 | 414 |
| 80 | 5.62 | 5.4 | 5.5 | 162 | 324 | 300 | 21.09 | 20.4 | 20.7 | 216 | 422 |
| 90 | 6.32 | 6.1 | 6.2 | 166 | 330 | 325 | 22.85 | 22.1 | 22.4 | 221 | 429 |
| 100 | 7.03 | 6.8 | 6.9 | 170 | 338 | 350 | 24.61 | 23.8 | 24.2 | 225 | 437 |
Corrosive Steam
When the water used to generate steam contains dissolved air, oxygen or carbon dioxide, these gases end up as contaminants in the steam. At the high temperatures of steam both oxygen and carbon dioxide are extremely corrosive.
Carbon dioxide is acidic and therefore attacks metals, whereas the oxygen corrodes metals and oxidizes rubbers. Corrosion of metals in the presence of both oxygen and acids is forty times faster than with either alone.
Boiler water is therefore normally treated not only to remove the "Hardness" which would cause "furring" of the boiler but also to remove dissolved oxygen and carbon dioxide and to ensure that the steam is not only not acidic but even slightly alkaline. Boiler water treatment is a specialized subject beyond the scope of this booklet but correct steam generation is important as we shall see in the next section.
Deterioration of Steam Hose
Like all rubber products steam hoses have a finite life and are subject to gradual deterioration with use. However, it sometimes happens that hoses which have been given a good life suddenly start failing without apparent reason. In such cases, it is often a change in the steam conditions causing a rapid acceleration of the normal failure mode.
It is therefore useful to consider how long steam hoses normally last and thus how the condition of the steam affects hose life.
The content, material and data contained herein is product of the Kuriyama Corporation. JGB Enterprises, Inc. is merely submitting this information to all our customers interested in buying Kuriyama products. It is the intent to provide our customers with as much information as necessary, to help them make an educated decision in purchasing Kuriyama hose products.















